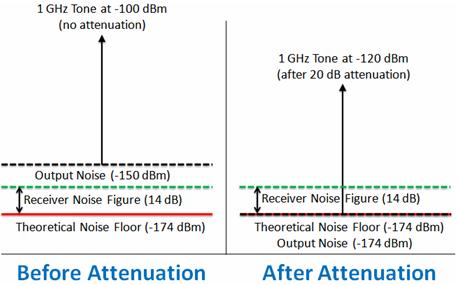
Theoretical Noise Floor

In radio communication and electronics this may include thermal noise black body cosmic noise as well as atmospheric noise from distant thunderstorms and.
Theoretical noise floor. Noise is always present and received on a radio even when no wanted signals are present. In signal theory the noise floor is the measure of the signal created from the sum of all the noise sources and unwanted signals within a measurement system where noise is defined as any signal other than the one being monitored. To predict the sensitivity of a receiver design it is critical to understand noise including enbw. The level of the noise floor determines the lowest strength signals that can be received and therefore the.
The equivalent noise bandwidth enbw is a way to understand the noise floor that is present in these filters. The noise voltage across the matched input terminal is. Noise floor db 1 76 6 02 bits of resolution 10log10 waveform output points. A typical radar receiver would require a s n of 3 to 10 d b to distinguish the signal from noise and would require 10 to 20 db to track.
A skilled operator might only be able to distinguish a signal 3 db above the noise floor s n 3 db or 75 dbm. Noise floor the typical way to define the minimum detectable power of a detector is by a measure of the noise equivalent power nep given in units of w hz1 2. Mean noise pow er would be 174 dbm 10 log 4x10 9 174 dbm 96 db 78 dbm. There are established theoretical noise floor limits for electronic equipment.
Even a simple resistor or any source of resistance in a circuit will produce noise. Subtract ktb from the normalized nyquist band noise power. Basic thermal noise calculation and equations. Calculate the input noise of the converter which is the theoretical thermal noise floor limit ktb 174dbm at room temperature.
The power available from the source is. In addition to this there is an online calculator to provide additional assistance. To calculate the thermal noise levels there are formulas or equations that are relatively straightforward. Thermal noise is effectively white noise and extends over a very wide spectrum.
The noise floor of a receiver is an important aspect of its operation as it gives a guide to the level of the minimum signal that can be received. Nep is caused mostly by shot noise from the statistical nature of photons and has been defined as the optical power. This paper will cover each of the building block characteristics used to calculate receiver sensitivity and then put them together to.
















.jpg)