Thermal Conductivity Of Air At Room Temperature
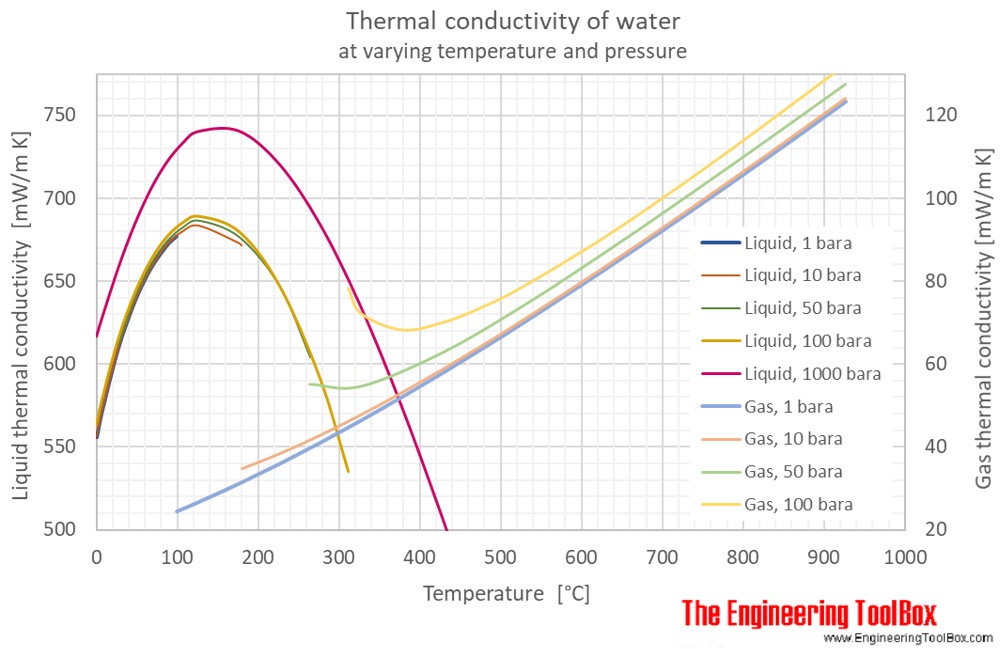
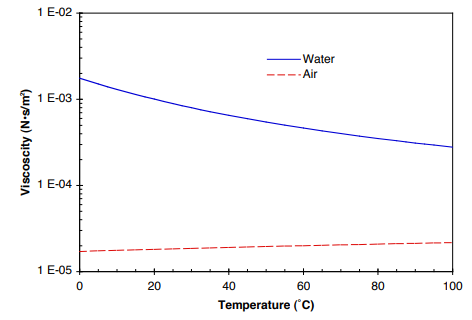
Air thermophysical properties thermal properties of air density viscosity critical temperature and pressure triple point enthalpi and entropi thermal conductivity and diffusicity and more air conditioning cooling of air and generated condensate water may condensate when air is cooled in an air conditioning system.
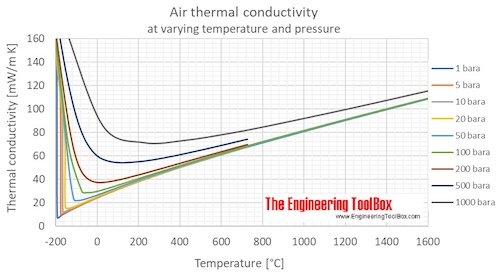
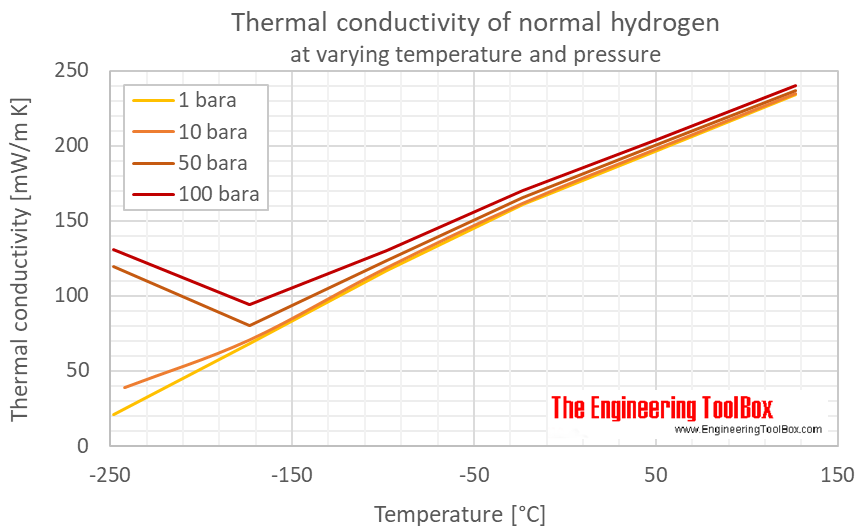
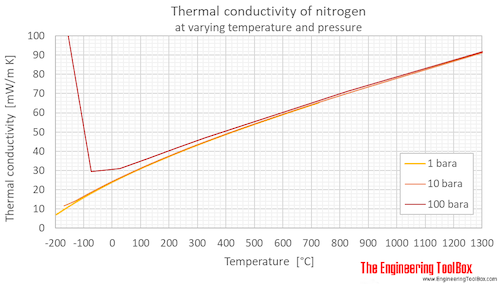
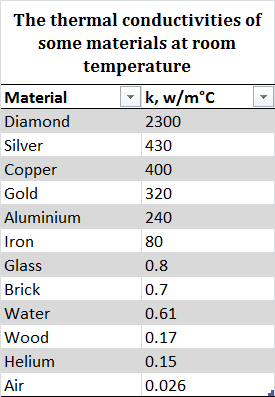
Thermal conductivity of air at room temperature. Steady state and transient steady state techniques infer the thermal conductivity from measurements on the state of a material once a steady state temperature profile has been reached whereas transient techniques. Notable exceptions are helium 0 15 and hydrogen 0 18. This chart gives the thermal conductivity of gases as a function of temperature. The notation p 0 indicates the low pressure limiting value is given.
With growing temperature the thermal conductivity goes through maximums which are connected with maximum heat transfer by the heats of respective reactions. Unless otherwise noted the values refer to a pressure of 100 kpa 1 bar or to the saturation vapor pressure if that is less than 100 kpa. Broadly speaking there are two categories of measurement techniques. There are several ways to measure thermal conductivity.
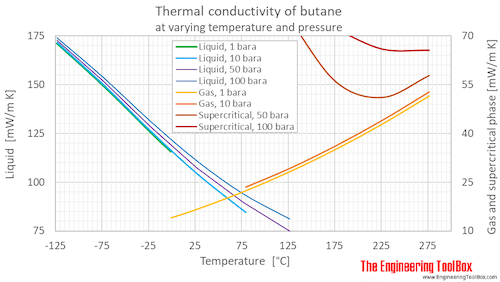
At low pressures and high temperatures the thermal conductivity sharply increases due to dissociation. Each is suitable for a limited range of materials. Air density specific weight and thermal expansion coefficient at varying temperature and constant pressures online calculator figures and tables showing density specific weight and thermal expansion coefficient of air at temperatures ranging 100 to 1600 c 140 to 2900 f at atmospheric and higher pressure imperial and si units. Air thermophysical properties thermal properties of air density viscosity critical temperature and pressure triple point enthalpi and entropi thermal conductivity and diffusicity and more butane specific heat online calculators figures and tables showing specific heat cp and cv of gasous and liquid butane c 4 h 10 at.
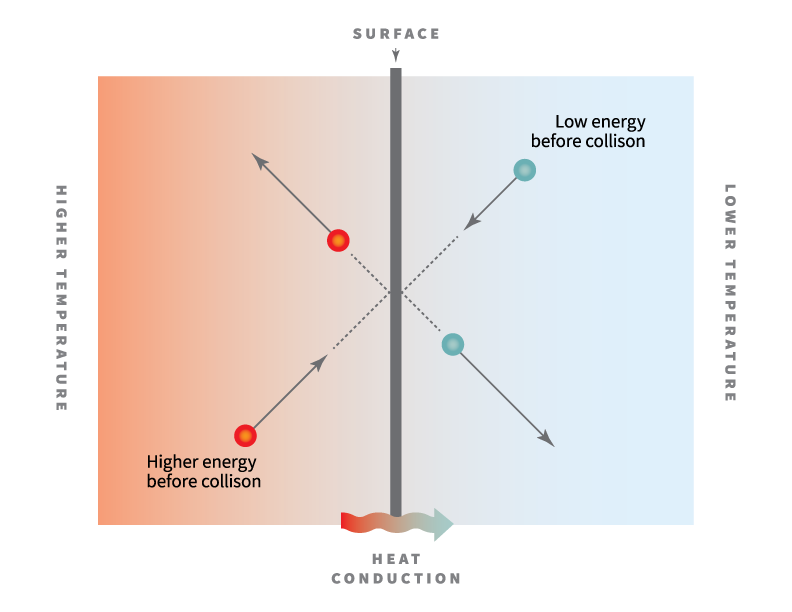
The most common theoretical explanation of heat conduction in gases is provided by the kinetic gas theory which treats the collisions between the atoms or molecules as the. Thermal conductivities of air at dissociation conditions are given in table 6.